Rights and obligations of conscripts in the Russian Federation
According to the law, every young man of military age must appear at the commissariat upon request. The summons issued by the Commissioner will indicate the date and time and must be adhered to.
Important: if a young man has legal grounds for receiving a deferment, he must comply with the requirements of the commissariat and provide evidence of his rights to a deferment.
The young man’s responsibilities include passing a medical examination. If the result is negative, he has the full right to receive the status of unfit for military service and receive a supporting document.
Citizens of military age have the following rights and responsibilities:
- receive a summons against receipt;
- comply with military registration requirements;
- appear at the military registration and enlistment office upon summons for a medical examination, training and transfer to the place of duty.
In case of failure to appear at the appointed time on the summons, the citizen is considered an evader, and from that moment he becomes liable.
What is service evasion and who are draft dodgers?
A draft dodger is a person who, having legal obligations to serve in the army, fraudulently rejects the commissariat’s requirement to appear and undergo a medical examination.
To understand what it means for a young man to evade military service, you should step by step understand the order of mandatory actions of a conscript:
- receipt of a summons for mandatory attendance at the commissariat, this does not have to be a conscription into the Armed Forces, the requirement may be associated with a mandatory routine medical examination;
- attendance according to the specified date and time;
- passing a medical examination to determine the fitness category;
- receiving a summons for military service and complying with the requirements.
Important: evasion of any of the listed points is a gross violation of the regulations and entails liability.
Only a valid reason, supported by documentation, can relieve a conscript from liability.
After receiving the summons, the young man is obliged to appear at the military registration and enlistment office
Types of Evasion
- From receipt of the summons. The conscript is obliged to accept the summons and sign for its receipt, but only if the procedure takes place in the manner prescribed by law. If dad signed, then let him join the army instead of his son. A young man who refuses a summons and does not sign for its receipt comes to the attention of not only the military registration and enlistment office, but also law enforcement agencies, and the police do not have the right to put any pressure on the conscript, arrest him or take him to the police station.
- From medical examination. If a citizen receives a summons and signs, this means that from that moment “his soul and body” belong to the state. Consequently, he is simply obliged to appear on the appointed day and time for the military medical examination. He will not be considered a draft dodger if he was unable to appear for a medical examination for valid reasons, the existence of which requires documentary confirmation.
- From further examination. If a conscript does not want to undergo additional examination, he must write a reasoned refusal. If the draft commission does not find intent to evade conscription in his actions, the young man will pay a fine of 500 rubles. If the refusal to undergo further examination is unmotivated and aimed at evading conscription, the punishment for this may be more severe.
- From reporting to the assembly point. If a citizen does not agree with the draft commission, then he must still sign the “combat” summons, otherwise his complaint against the action/inaction of members of the draft commission will not be considered by the court. Failure to appear on such a summons is possible only if the decision of the draft commission is appealed in court or if there are very good reasons. A young man who fails to show up at the recruiting station faces punishment - either administrative or criminal.
Ways to evade military service
In most cases, the following reasons push young men to take the step of evading conscription for military service:
- refusal to accept a summons against signature. A summons was brought home to the young man, and he went out, but refused to receive the document;
- failure to appear on a summons received against signature at the military registration and enlistment office without good reason. If the summons was sent by mail as an urgent notification, it cannot be considered that the man evaded, since there is no evidence that he personally received the letter;
- deliberate self-harm, such as concussion, broken limbs and others;
- obtaining a medical certificate of unfitness for service through corrupt means;
- moving from the actual place of residence, not making changes to the place of registration. Traveling abroad is the most common way today;
- failure to appear at the military registration and enlistment office after the end of the deferment period without good reason.
Important: to ensure that the real reasons for the delay are not recognized as evasion, documentary evidence of their existence should be provided in a timely manner. You also need to know the rules for obtaining a document - against signature personally by the conscript or an authorized person, for example, a relative.
Legitimate reasons for deferment and release
The topic of legal refusal to serve in the army is widely researched on the Internet. Many businessmen offer several “legal” ways of helping in evading service, in particular among such methods are the following:
- Exemption from the army due to medical standards. According to the regulations, there are a number of diseases in the presence of which a conscript can be considered partially fit and receive category “B”. Then he will not need to serve, and the businessmen promise to assist in obtaining such a medical opinion.
- Caring for a sick relative. This is possible if you have a relative who is able to obtain a positive conclusion based on the results of a medical examination about the need for the care of a third party. That is, the partial incapacity of a relative provides a deferment from the army; it can be obtained several times. The relative should not be fully supported by the state.
- What else do experts recommend? Wife's pregnancy: if there is one young child and the wife is more than 26 weeks pregnant, the conscript receives a deferment.
- Independently raising your own child (single father) or young brother/sister.
Important: if these reasons are abused to obtain a deferment, citizens bear administrative, and in some cases, criminal liability.
Many people try to “refuse” from the army already in the process of serving, for example, they escape or cause serious injuries to themselves.
Commentary to Art. 328 Criminal Code
1. The objective side of the two crimes provided for in the article is expressed in inaction.
2. Legal grounds for exemption from conscription for military service are: recognition of a person as unfit or partially fit for military service due to health reasons; the presence of an unexpunged or outstanding conviction for committing a crime, etc.
3. Evasion of conscription for military service (Part 1) is formed by: a) the conscript’s refusal to receive a summons from the military commissariat or to send a draft commission against receipt; b) his failure to appear at mandatory events related to conscription for military service (for medical examination and examination, at a meeting of the draft commission, at the gathering place for sending to the place of military service); c) unauthorized leaving by a conscript of a collection point before being sent to the place of military service, with proper notification of the conscript and the absence of legal grounds for exemption from service; d) a conscript fraudulently obtains exemption from military service as a result of feigning illness, causing himself any harm (self-mutilation), forgery of documents or other deception.
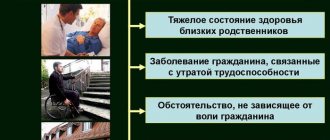
A necessary condition for liability for failure to appear on time for events related to conscription is also the absence of valid reasons. Valid reasons in these cases, provided they are documented, include: illness or injury of the conscript associated with loss of ability to work; the serious health condition of his loved ones (father, mother, wife, son, daughter, etc.), participation in the funeral of these persons; an obstacle arising as a result of force majeure, circumstances beyond the control of the citizen; other reasons recognized as valid by the draft commission or court.
4. Evasion from performing alternative civil service (Part 2) is possible from the moment it begins - the day the citizen leaves for the place of service specified in the order of the military commissariat, until the end - the day the employer terminates the employment contract with the citizen upon his dismissal from service. The objective side of the crime is formed, in particular, by failure to appear without good reason at the place of alternative civil service within the time period specified in the order, refusal to enter into a fixed-term employment contract, early dismissal from alternative civil service by deception, unauthorized abandonment of the place of work (workplace).
5. Crimes provided for in Art. 328 of the Criminal Code are continuing. If a person fails to confess or is not detained, they end due to the disappearance of obligations for conscription into military service or alternative civilian service. This moment is considered to be when a person reaches the age of 27 years, after which the duties of military service cannot be assigned to him, or the age that is the limit for being in alternative civil service (28 years 9 months or 28 years 6 months, depending on its duration). After reaching the age of 27, persons who committed this crime before the specified age may be subject to criminal prosecution for evading conscription for military service, provided that the statute of limitations for bringing them to criminal responsibility has not expired.
6. The subjective side of the crime provided for in Part 1 is characterized by the goal of avoiding the imposition of the obligation to perform military service upon conscription. It does not matter whether the conscript was only avoiding the next conscription for military service or had the goal of completely avoiding conscription.
When committing a crime under Part 2, the person has the goal of completely evading the duties of the alternative civil service. Evasion from performing alternative civil service for a certain period (for example, one month), after which the person returns to the place of performing alternative civil service, does not constitute a crime. In this case, the person may be subject to disciplinary action.
7. The subjects of the crime provided for in Part 1 are conscripts - male citizens who have reached the age of 18, who are or are required to be registered with the military and who are not in the reserve, subject to conscription for military service in accordance with the procedure established by law. The subjects in Part 2 are persons obliged and undergoing alternative civil service, i.e. special subjects.
The procedure for dealing with draft evaders
If a young man is not at home, or cannot be found at his place of study or work, representatives of the military registration and enlistment office begin to act decisively.
The search for the evader begins - documents on him are transferred to the investigative committee. After studying the received materials, the investigator sends a summons to appear before him. If the summons does not reach the addressee, a case is opened against the conscript in accordance with the regulations of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. The young man is put on the federal wanted list.
If you evade conscription, the military registration and enlistment office transfers materials to the investigative committee
The search continues actively, and the investigator quickly receives results. Any use of a bank account or work record helps to locate the evader's location.
Further, depending on the degree of guilt, the young man is held accountable and punished, which may be as follows:
- a fine for evading military service in the amount of 200,000 rubles or average monthly income for a period of up to 18 months;
- arrest for a period of up to six months;
- imprisonment for a period of up to 2 years.
Important: criminal liability occurs only if the presence of signs of evasion is fully proven in court.
Additional examination
In some cases, a medical examination alone is not enough to determine the diagnosis or issue of a citizen’s suitability for military service. Then the military registration and enlistment office sends the conscript for an optional examination. You can refuse this if you write a corresponding statement. However, you need to understand that it is not considered an evasion of medical examination and conscription in general.
If a person does not come for examination, then, depending on the intent, the punishment for evasion will be administrative or criminal.
Responsibility for draft evasion
It should be remembered that representatives of the military registration and enlistment office must prove the fact of evasion, otherwise they cannot bring the conscript to justice. A young man can be threatened with liability as much as he likes, but in order to actually bring him to justice, an investigation must be carried out and it must be proven that he has violated the rules.
Responsibility can be criminal or administrative, each is used in a specific case and entails certain consequences.
Administrative responsibility
The Administrative Code has a separate article on offenses committed by conscripts. This responsibility is brought to bear on the following points:
- Failure to fulfill obligations for military service - penalties are applied for deliberately concealing the place of one’s stay, traveling abroad, changing the place of registration. Failure to appear at the military registration and enlistment office for a medical examination upon request. Silence regarding changes in family status, education, place of work.
- Avoidance of examination by a medical commission, ignoring the requirements of the military registration and enlistment office to obtain a doctor's opinion and, accordingly, a suitability category. In this case, penalties from 100 to 500 rubles are also applied.
- Deliberate damage or loss of military documents (summons, ticket and others intended to indicate the status of a young man). Fine from 100 to 500 rubles.
Penalties may vary depending on the region, as if based on the economic well-being of the population. For example, in Saratov the average fine for evading service is 9,000 rubles, but in Moscow it can reach 50,000 rubles.
Criminal liability
Criminal liability is fully regulated by Art. 328 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation and appears as a result of avoiding military service.
According to its norms, evasion of service is punished severely, from 2 years of forced labor to 6 months of arrest.
In addition, when making decisions, courts often use the norms of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation of 2008, which describes in detail all the main types of punishment for leaving the army.
Based on this legislative act, judges take fairly harsh penalties. An example of this is the sentence of imprisonment for a year in a maximum security colony, which was announced in 2018.
Grounds for administrative liability
A pre-conscription conscript, and even more so a conscript, must inform the military registration and enlistment office about all significant and significant changes in his life, since such information may affect conscription.
A citizen liable for military service is punished with a fine of 500 rubles in the event of:
- Failure to appear at the military registration and enlistment office for registration or deregistration;
- Failure to notify military commissariat employees about leaving the locality for a period of more than 3 months;
- When traveling abroad for a period of six months or more;
- When moving to another city or changing place of work/study and not notifying about it.
The same punishment awaits someone who treats documents carelessly, for example, who deliberately spoiled a registration certificate. Even the first and only refusal to undergo a medical examination is punishable by the same “magic” amount of 500 rubles. Why is that? Because such offenses are classified as light, and sometimes even one detailed conversation is enough to convince a citizen liable for military service that the law cannot be broken, and subsequent offenses of a similar nature can bring him to the dock.
In what cases is punishment applied to evaders?
From everything it follows that evading the army is quite dangerous and strictly punishable. Every young person must be aware of his actions, and even more so bear responsibility for them.
It is important to understand that any secret place when a guy is put on the federal wanted list will be revealed and he will be put on trial. Upon receipt of the case, the Investigative Committee will do everything possible to bring the young man to justice and prove his guilt.
And if, due to his age, the child is arrogant, parents should take this point into account and prevent him from becoming responsible. In addition, the stamp of a criminal record will ruin the young man’s reputation forever, and it will be difficult to realize one’s career and social potential.
Important: when falsifying documents, such as a medical examination report, you should remember that they will be thoroughly examined, and when proving a criminal case, responsibility will be appropriate.
If the realization of what was done came late and the deed has already been done, you should try to alleviate your guilt, to do this you need to turn to a lawyer for help and come to the military registration and enlistment office with repentance.
If you receive a verdict, you should also not despair; every citizen has the right to dispute the court’s decision. There is a standard 10 days for this after the verdict is announced.
Advice: the participation of a specialized human rights activist in the case and personal repentance in most cases leads to a suspended sentence for the evader.
Valid reasons for failure to appear on a summons
Often, conscripts, not knowing the norms of the law and having good reasons for being in civilian life, simply begin to ignore the requirement of the commissariat, do not come when requested, or even come up with ridiculous and ridiculous excuses.
Meanwhile, they have a legal basis for the delay; they just need to document it. The legal grounds regulated by the regulations are as follows:
- illness or injury resulting in temporary or permanent loss of ability to work;
- serious health problems of a close relative;
- death of a loved one;
- independent obstacles - disasters, weather events, accidents, etc.;
- full-time study at a higher educational institution;
- the status of a candidate of sciences eliminates the need to serve in the army at all;
- graduation from the military department during basic training;
- completion of alternative civil service;
- the wife's pregnancy with her second child;
- father of a large family;
- guardianship over an incapacitated relative or minor brother/sister.
In addition, there are reasons that the military registration and enlistment office considers individually and makes a decision at its own discretion.
Documented reasons for a youth’s failure to appear are exempt from liability for evading military service.
In what cases can you avoid punishment for failure to appear on a signed summons at the military registration and enlistment office?
According to the current Federal Law No. 53 of the Russian Federation, there are several reasons why failure to appear on time at the military registration and enlistment office will be considered valid:
- Loss of ability to work due to illness, injury;
- Natural disasters, catastrophes, force majeure circumstances;
- The need to care for immediate family: spouse, brother or sister, children, parents, grandparents;
- Other reasons and circumstances, the degree of respect for which is determined by the court and the draft commission.
It should be taken into account that all the above-described reasons for failure to appear at the military registration and enlistment office must be confirmed by official documents. Thus, illnesses and injuries are confirmed by a certificate or extract from a health care institution, the death of a loved one by a death certificate, natural disasters by a certificate from the local administration.
It is also worth mentioning that forgery of documents is punishable by law. If exposed, you may face criminal liability.
Statute of limitations under the article for evasion of military service
Regardless of the type of punishment chosen by the court, a conscript can receive exemption from liability in accordance with Art. 78 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. There is a release from liability due to the expiration of the statute of limitations.
The person who committed the offense is released from liability if:
- 2 years have passed since its commission;
- minor crime.
That is, if the conscription age is 18–27 years old, and a person committed a crime at 27 years old, then when he reaches 29 years old, responsibility is removed. A citizen can only be involved if the deadline has not expired.
Responsibility is also removed from the conscript if circumstances change.
For example, a conscript received a summons against signature and did not appear at the military registration and enlistment office. There was a search and investigation, but there was no conscript. And only after 1.5 years the search operations were crowned with success. However, the conscript provided a document stating that he is a first-year student at the university. Circumstances have changed, which means there is no responsibility.
Nuances
All decisions regarding the sentencing of a draft dodger are made by the court, which analyzes the actions of the conscript and looks for intent in them. If a citizen did not come to the military registration and enlistment office on time, but still deigned to pay a visit there before the end of the conscription, then the court will definitely take this fact into account, and the failed draft dodger can “get off” with a fine of 500 rubles. And if the guy had a good reason, then he is completely freed from all responsibility and goes into the army with a pure heart.
If the conscript did not sign the summons and, of course, did not appear at the recruiting station, or the summons was handed to him in violation of the law, then he will definitely not bear criminal liability for such evasion. That is, the court will consider that the citizen was notified inappropriately, which is a serious violation on the part of those responsible. It is worth noting that any deliberate refusal to perform military duty to the country is punishable.
And even if a real punishment is imposed, after expunging the criminal record, the young man will still be drafted into the army, if by that time he has not passed the conscription age. It is possible that the guy will not have to run from the military registration and enlistment office, because it may turn out that he is not fit for military service at all. This is why it makes sense to undergo a medical examination.
Legislative documents on the topic
The entire issue of conscription into the army is regulated by the following regulatory documents:
- Federal Law-53 of 1998 indicates the conscript’s obligations to appear at the appointed time upon request;
- in Art. 7 of this document lists valid reasons, in the presence of which a young man has the right to receive a deferment from military service;
- Art. 31 Federal Law “On Military Service” indicates signs of evasion of conscript duties;
- Art. 21.5 of the Administrative Code of the Russian Federation indicates the administrative punishment of a conscript and the cases when it is applied;
- Art. 21.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses determines penalties for certain types of violations;
- Art. 328 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation designates criminal punishment for a conscript;
- clauses 1 and 2 art. 328 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation regulates in detail the options for punishment for offenses committed by young men;
- Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation No. 3 indicates the possibility of bringing to criminal liability only young men aged 18 - 27 years;
- Art. 338 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation indicates options for punishment for desertion;
- Art. 337 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation prescribes punishment for AWOL;
- Art. 339 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation provides for punishment for feigning illness during service.