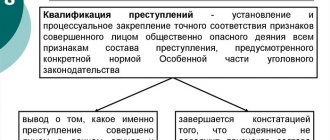
How is it determined?
The legislator directly links the statute of limitations and the category of crime. Crimes, by their nature and the inherent degree of danger to society for each of them (and, accordingly, the maximum sentence in the form of placement in a prison camp) are divided into four categories.
For each of them, the period during which the perpetrator of illegal actions can be brought to criminal liability is clearly named. Article 15 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation speaks about the categories of crimes.
Statutes of limitation and issues of exemption from liability in connection with their expiration are announced in Article 78 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation:
- Acts of minor gravity are crimes committed intentionally or through negligence, for which punishment is provided for no more than three years in prison. For such crimes, the statute of limitations is two years.
- Crimes in the category of medium gravity are acts that were committed with one type of intent or another and for which the maximum punishment does not exceed five years in prison. This group also includes reckless crimes, for which the law prescribes punishment of more than three years of isolation of the convicted person from society. The statute of limitations after the commission of such an act is calculated at six years.
- Crimes classified as serious can only be intentional . Punishable by up to ten years in prison. The period for possible prosecution of the culprit from the moment the criminal act was committed is 10 years.
- Particularly serious crimes are also committed only with intent. They are subject to strict sanctions in the form of imprisonment in correctional institutions (PI) for a period of more than ten years or even more severe punishment. The statute of limitations for such crimes, of course, is the longest and is fifteen years.
Reference . If we are talking about crimes for which the law has established life imprisonment as a sanction, then the issue of statute of limitations is determined only by the court.
If the court does not consider it possible to release the offender from criminal liability due to the fact that many years have passed, then life imprisonment in this case is excluded (the punishment will be expressed in imprisonment in the prison for a certain period).
In addition, in Part 5 of Art. 78 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation lists a number of articles for which statutes of limitations are not applicable in any case . These are crimes against public safety (armed rebellion, terrorism, encroachment on the lives of government or public figures, etc.).
From our separate articles you will learn how penalties are classified and what liability is provided in cases of theft:
- money and documents;
- state property and budget funds;
- weapons and ammunition.
When does Article 78 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation apply?
According to current legislation, Article 78 of the Criminal Code can be applied at different stages of the criminal process:
- At the stage of preliminary investigation, unless we are talking about a particularly serious criminal act.
- At the time of transfer of the case to the court of first instance. In this case, it is necessary to file a corresponding petition addressed to the judge during the preliminary hearing.
- During the trial. This also requires filing a petition addressed to the presiding judge, but first obtaining the permission of the defendant.
This provision can be applied at any stage of criminal proceedings, even after the verdict has been announced by the court of first instance. All that matters is that the sentence does not enter into legal force.
It is important to understand that the court is not at all interested in applying the provisions of Article 78 to murderers. Thus, everything depends on the correct actions of the lawyer. If he does not even manage to achieve the application of the norm in question, but he does everything correctly, then he has the opportunity to file a cassation appeal. During the cassation hearing of the case, the judges will pay attention to the actions of the defense that are correct from the point of view of the law and will overturn the verdict of the lower court by applying the provisions of Article 78.
Statute of limitations for theft
Let's figure out what the limitation periods are for unqualified (simple) thefts and thefts with qualifying characteristics.
Unqualified theft of property
"Simple" theft. It did not entail significant damage to the victim (from 5,000 rubles), was not associated with penetration into the home, theft from a bag or pocket of outerwear, etc. This is the most common category of theft . An example would be theft from a store of small equipment (for example, an inexpensive phone costing from 2,500 to 5,000 rubles).
Also, theft from a home will be classified as simple if the owner himself allowed the thief into the apartment (for example, he took advantage of his trust by introducing himself as a plumber). Such theft carries a maximum penalty of two years in prison. Therefore, this is an act of minor gravity. The statute of limitations is two years from the moment the theft was committed.
Read more about what petty, simple theft means and in what cases it is punishable under the Code of Administrative Offences, and when under the Criminal Code.
Moderate
This is already theft with qualifying features . They are:
- there was illegal entry into the premises or other storage;
- the act was carried out by prior conspiracy by a group of persons;
- the criminal act caused significant damage to the victim or legal entity;
- the theft was carried out from a citizen’s carry-on luggage or clothing (we wrote more about pickpocketing here).
For example, a separate barn was broken into (breaking into a room or storage area), and rabbits were stolen from it by the attacker. Or a bicycle worth 10,000 rubles has been stolen - significant damage (read more about the theft of a bicycle here). Or the wallet that was in the victim’s handbag was stolen. For such acts, the legislator provided for the placement of the offender in a prison cell for a period of up to five years.
These crimes are classified as medium in severity, which means that the period for prosecution will be six years from the date of the illegal act.
Severe
Describes theft with such qualifying features as:
- illegal entry into a home;
- large amount of damage (from 250 thousand);
- theft from oil, gas, and petroleum product pipelines;
- theft of funds from a bank account or theft of electronic money (for example, WebMoney or Yandex Money).
An example could be a burglary of a door to an apartment, or a secret theft of property worth more than 250 thousand rubles, or a situation where a criminal tap into an oil pipeline was committed and oil was stolen from there. The Criminal Code provides for imprisonment for such criminal acts for up to six years.
We see that this is also a serious crime, and the period during which criminal prosecution is possible is ten years .
Particularly large or committed by an organized group
Theft, which was committed by an organized group or causing particularly large damage (we are talking about an amount of one million rubles).
Such actions are punished severely by law : the perpetrators can spend up to 10 years in prison (read more about criminal liability for theft provided for in Article 158 of the Criminal Code here). For such crimes, the perpetrator can also be held accountable for up to ten years.
An example would be the theft of a car worth over a million rubles for the purpose of its further sale (it is important to distinguish it from theft without the intent of theft - Article 166). If a car worth less than a million is stolen (not stolen, for theft there is a separate article 166 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation), but the theft of the car was committed by an organized group of persons (for example, regularly engaged in such acts), then this is also part 4 of article 158.
Attempted murder
Attempted murder, of course, can be classified as a serious prohibited act, for which the criminal norms of the Russian Federation provide for appropriate types of punishment.
The very concept of “attempt” means the absence of a direct result, which was previously intended by the organizer of this act. But, at the same time, it presupposes the obligatory presence of deliberate intent, in which the person knew about the subsequent negative consequences and really wanted them to occur.
In order for an attempt to be recognized as such, it must have all the established signs of a dangerous act. The main features include the following:
- the presence of a direct object. In this case, the object is the life of a citizen, on which an attempt is made;
- definition of a subject - a person who commits an attempted murder. In this case, they must be a person who has reached the age of majority and also has full legal capacity;
- subjective side. Attempted murder must be characterized by the presence of proven premeditation in the actions of the accused. If this circumstance is not properly confirmed, the application of a certain penalty will be unlawful;
- the objective side is determined by the presence of specific external signs that can confirm the entire composition of unlawful actions.
The penalty for attempted murder will certainly be imprisonment. The exact period depends on the immediate circumstances of the case, as well as on the presence or absence of aggravating factors.
The legislation of the Russian Federation establishes a certain period of limitation in relation to such a dangerous act as attempted murder. According to general rules, it will be 15 years. The starting point in this case will also be the moment when the attempt was committed.
If the violation of criminal norms was committed over an extended period of time, the last prohibited act is taken into account.
Author of the article
Dmitry Leonov
Work experience 15 years, specialization - housing, family, inheritance, land, criminal cases.
Author's rating
721
Articles written
712
about the author
When does the deadline count?
The beginning of the period from which the countdown of the period during which the offender can be held criminally liable begins the day after the commission of the criminal act.
The end of the period during which the offender is brought to justice occurs:
- After the judge makes a decision on the case and it comes into force;
- After the statute of limitations for the crime has expired;
Info
If a criminal is found to have committed several crimes, then the statute of limitations for each is calculated separately.