Why is it necessary to know what is the difference between robbery and robbery? The differentiation of these crimes is necessary, first of all, for the correct qualification of an unlawful act.
The similarity of these criminal acts lies in the common object of encroachment - the right of ownership, which is why many are confused about these crimes.
However, there are differences in the following criteria:
- the severity of the crime committed;
- method of commission (corpus delicti: objective side and other optional features);
- measure of responsibility;
- other.
In order to understand this issue, it is necessary to refer to the definition of these criminal acts, which are enshrined in the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation , as well as other regulatory legal acts, including the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court on delimitation (there were no changes in 2022).
Definition of the concepts of “robbery” and “robbery”
Robbery refers to the unlawful taking of someone else's property. A person acts openly and deliberately with the use of violence or the threat of its use, which does not pose a danger to the life and health of the victim (Article 161 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
The socially dangerous consequences of robbery lie in the fact that the process of criminal encroachment is considered completed at the moment when there is a real opportunity to take possession and use someone else’s property.
Robbery refers to the unlawful taking of someone else's property. A person acts openly and with the use of violent actions or the threat of their use, which are dangerous to life and health (Article 162 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
Of all crimes against property, robbery is considered the most serious illegal act.
Robbery can be qualified from the time the illegal actions began. This crime is characterized by a truncated composition, since for qualification it does not matter whether it was completed or not. This exceptional feature occurs because the criminal’s actions are aimed primarily at the most significant object - life and health, and only then at property. This is the essence of the crime - this object is protected by law and the state to the greatest extent.
From the objective side, robbery is committed openly and with the use of violent actions that are dangerous to the life and health of the victim, who may not see the attacker at the time of the attack.
When does the crime not constitute a crime?
We already know how robbery combined with violence differs from robbery, but not all acts can be classified as a crime. In some cases, when all the signs of an incident are present, the behavior of the perpetrator cannot be classified as a crime. Sometimes theft may not be considered a crime. In this case, it is important to note such a concept as appropriation of a found thing. In this case, there is no corpus delicti; it is only important to determine whether the item was forgotten or lost.
A lost item is an item that has no signs of identification and is located in a place that is unknown to the owner. A watch lost in the forest will be a find, but a car left unattended will not.
Difference between robbery and robbery
PPVS about theft, robbery and robbery provides a distinction between criminal acts according to the following components included in the objective and subjective side:
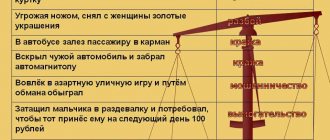
1. Socially dangerous act. In robbery, the attacker encroaches on property, and violence is used against the victim, which is dangerous to his life and health. Therefore, another object can be human life and health. During robbery, theft occurs in a manner that does not pose a danger to life and health.
2. Intent. If a person, when committing theft, deliberately uses violent methods that can have negative consequences for the life and health of the victim, then this act is classified as a robbery. But during robbery, violent actions may not be used.
3. Socially dangerous consequences. Robbery has a truncated composition, i.e. is considered completed from the beginning of the illegal actions. In this case, it does not matter whether the person completed his intentions or not, or whether he received a real opportunity to dispose of the property. Robbery is characterized by its material composition, i.e. the consequences of the crime are expressed in the opportunity for the criminal to dispose of the stolen property.
4. Method of committing the crime. Robbery will take place if the theft is committed using obviously dangerous objects (any weapon). At the same time, the Plenum Resolution on theft, robbery and robbery equates to weapons objects that can cause dangerous damage - knives, razors, crowbars, axes, grenades and other devices. In addition, the victim must be aware of the danger to life of these objects, including imitation weapons, an unloaded pistol and other prototypes. If the victim at the time of the crime realized that the threat was being carried out by a “fake” weapon, then the act can be classified as robbery.
Definition
Robbery
- This is a deliberate attack by one or a group of persons on a person with the aim of taking possession of his property. In this case, violence or the threat of its use is used to implement criminal intent. Any objects that can cause significant harm to health can be used as weapons (gun, knife, baseball bat, rebar, etc.)
Robbery
- this is the deliberate, open, unlawful taking of someone else’s property, which can be committed using violence that is not dangerous to life and health. The fundamental point is the volitional factor: if the person carrying out the robbery threatens the victim or persons who suddenly caught him at the scene of the crime, or uses life-threatening violence, the act must be classified as a robbery.
Difference between violent robbery and robbery
The difference between violent robbery and assault lies in the method of using violent actions. In both cases, bodily harm is caused, but their nature is different.
In a robbery they are life-threatening, but in a violent robbery they do not pose such a danger.
As an example of the classification of crimes from judicial practice:
1. When a wallet is stolen from a victim’s bag in a public and crowded place, the victim notices this and makes every effort to prevent it. However, the kidnapper continues to act: he deliberately pushes the victim and runs away. This crime is characterized by the use of violence that does not pose a threat to life. Therefore it is classified as robbery.
2. The situation is similar to the first one, however, when the victim discovers the theft, the attacker takes out a baton and continues to commit the crime, striking him on the head. As a result, the victim's skull was fractured, thereby causing serious harm to his health. Due to the danger of the violence used, this act is classified as robbery.
Comparison
Thus, the key point of difference between assault and robbery is the intent of the criminal. If he not only allows the use of violence, but also one that is dangerous to life and health, uses it or threatens to use it, then we are talking about a robbery. If in the process of committing a robbery the victim began to resist, and he used a knife, a stone or his own physical force to suppress it, then this will also be considered a robbery attack.
In terms of the severity of the crime, robbery is higher than theft, but lower than assault. The crime is considered completed at the moment when the criminal has the opportunity to dispose of the stolen property. A robbery attack is already complete at the moment it takes place. The combat properties of weapons themselves are not always important for assessing what they have done. An attack with a toy gun will also be robbery if the victim has reason to fear that it will be realistic.
Organization and methods of investigation
In the investigation of these criminal acts, their forensic characteristics are important - this is a set of data that allows one to properly conduct an investigation and work out investigative theories.
Theft by robbery and robbery pose the greatest danger to society, since they are committed with the use of violent actions, dangerous and not life-threatening. When committing these criminal acts, a person carries out a number of preparatory measures:
- exploration of the crime scene;
- studying the future victim;
- preparation of weapons and methods of execution;
- organizing methods of approach and departure (involving accomplices for help, preparing a vehicle, etc.);
- preparing the place where the stolen property will be stored;
- sales places.
When investigating these property crimes, it is necessary first of all to study the place where the theft took place. There it is also necessary to look for traces that could have remained from the kidnapper, subject to careful examination. Therefore, one of the main investigative measures is to inspect the scene of the theft, where any traces of the attacker can be found, including biological ones (fingerprints, traces of shoes, clothing, personal items, cigarette butts). All discovered items must be properly removed from the scene and entered into the protocol. After which the traces must be examined to find the possible thief or his accomplices.
It is also necessary to study the identity of the victim from whom the circumstances of the crime are being clarified. For the investigation, the victim’s method of movement and routes will be important, as well as the circle of people with whom the victim communicated (acquaintances, colleagues, neighbors). This will also make it possible to determine the circle of persons possibly involved in the theft.
Many crimes against property are solved without any delay, when the attacker did not have time to hide from the investigative authorities in a pre-prepared place and sell the stolen property.
Main differences between criminal acts
The ability to distinguish between different crimes is extremely important for an investigator or other law enforcement official.
This need is due to the fact that different types of criminal acts have different punishments. Let's look at the main difference between robbery and robbery, and for this we will highlight the following points:
| Criteria for highlighting differences | Robbery | Robbery |
| The crime poses a public danger | A “misdemeanor” is committed in a way that is not dangerous to the well-being and life of citizens. | Threats and violence are used against the victim. |
| Presence of intent in the crime | Taking possession of someone else's property occurs with intent, but the perpetrator does not use violence. | A person deliberately uses violent methods. |
| The consequences of crime are dangerous for society | A person gets the opportunity to take someone else’s thing, and only after performing this action will the crime be considered completed. | An act may have a truncated composition when it does not matter whether the criminal completed his action and received the opportunity to take possession of the property. |
| Method of committing the crime | The act is classified as robbery if there was no weapon or the threat was made with a “fake” weapon. | During the theft, obviously dangerous objects were used, i.e. weapons or items equivalent to them. |
Based on the listed signs and characteristics, you can easily determine what form of criminal act we are talking about. You can also use examples from judicial practice. Additional information about the differences between the two types of crimes described is presented in the video:
Punishment of the guilty persons
These crimes, encroaching on the property of citizens, are among the most serious, since they have an additional object - life and health. Therefore, liability for these illegal acts will be the most severe.
The maximum penalty for qualified robbery under Part 3 (committed by an organized group or on an especially large scale) will be imprisonment for a term of 6 to 12 years . The crime is characterized as particularly serious. According to Part 1, an alternative sanction is provided for robbery: from compulsory labor to imprisonment for up to 4 years . According to this part, the criminal act is characterized as of medium gravity.
Robbery with aggravating circumstances, provided for in Part 4, is punishable by maximum imprisonment (from 8 to 15 years). Qualified robbery is a particularly serious crime. The minimum term of imprisonment is provided for the main elements of robbery: up to 8 years, which classifies it as a crime of medium gravity.
Video: Lawyer on the intricacies of the concepts of theft, robbery and robbery
Peculiarities of theft qualification: excess of the perpetrator
The excess of the perpetrator is understood as the commission by the perpetrator of a criminal act that was not covered by the intent of other attackers.
Example. A group of young people under 18 years of age, with the goal of enriching themselves at someone else’s expense, attacked their peers not far from the school. In their arsenal, the group of attackers had metal pipes with which they threatened to cause physical harm in order to take away the money. One of the teenagers refused to give the money voluntarily, so one of the attackers invited the others to beat him. He was refused this offer, after which he hit him in the head with a metal pipe. The victim fell from the impact, and the injury was not compatible with life.
The qualification of criminal acts of a group corresponds to robbery under Part 2 – by a group of persons. However, in this situation the excess of the performer is evident , since the group did not have a single intent to cause serious harm to health.
You can study in more detail the question of how robbery differs from robbery in the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court.