Arson of property can happen quite unexpectedly. This unpleasant phenomenon also affected my home last year. When I was informed about the fire and I arrived at the scene, the property had almost burned to the ground. After that, I made every effort to ensure that the criminals received the highest possible punishment. In this article I will talk about liability for arson, as well as what awaits individuals who did it unintentionally.
Damage to property: definition and types
The legal dictionary means that damage is the loss of the original quality of objects under the influence of external factors. Property is a set of material assets that are in the possession of individuals/legal entities, municipal authorities or the state.
Classification of circumstances of damage to someone else's property:
- according to the degree of damage caused (complete destruction, partial damage);
- by degree of intent (intentional, unintentional);
- by subject of the offender (adults, teenagers, employed citizens);
- on the subject of the violation (damage to personal property of individuals, property of organizations, municipalities, states);
- depending on the applicable legal norm (Administrative Code, Criminal Code, Civil Code or Labor Code).
Attention! Punishment is applied to guilty persons only after proving the guilt of the offender and the extent of the damage caused.
What is the penalty for arson under Article 167 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation?
Despite the fact that as a result of arson, the victim can instantly lose all his property acquired through back-breaking labor, the legislator classified this crime as an act of moderate gravity.
The maximum punishment provided for by the article for arson of someone else's property is 5 years in prison
The final punishment can be influenced by various factors: the presence of a criminal record, aggravating and mitigating circumstances, the amount of damage, actual consequences, etc. For example, for setting fire to a house that was the only home for an entire family, the amount of punishment can be noticeably more severe than for setting an old house on fire. broken car.
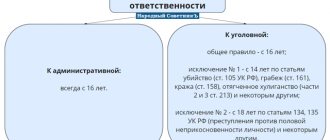
Administrative responsibility
Article 7.17 of the Code of Administrative Offenses specifies a violation in the form of deliberate destruction or partial damage to material assets. The fact of liability is not affected by the type of property in relation to which illegal actions were committed. The main thing is confirmation of the amount of damage caused. A citizen will be held accountable only when the assessment of damage does not exceed insignificant amounts, namely 5,000 rubles .
The only type of penalty applied to violators in this case is a fine. Its size varies between 300-500 rubles.
The punishment is assigned by the judge considering the material. A protocol on violation is drawn up by the police and submitted to the magistrate’s court of the locality.
Attention! For causing damage to property, according to the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, citizens who have reached the age of 16 can be held accountable.
When is an arson investigation scheduled?
To understand whether the arson was intentional or unintentional, an examination is carried out. Often the initiator of its implementation is an interested person.
For example, an insurance company conducts an examination to find out whether the car was set on fire intentionally or not.
After all, sometimes car owners themselves set fire to their cars in order to receive compensation payments from the insurance company.
Thanks to this examination, it is possible to find out:
- whether there were deaths as a result of arson;
- what amount of damage was caused to the property owner;
- at what time the fire occurred;
- what materials and methods were used to commit the arson;
- the fire was caused intentionally or unintentionally.
Responsibility under criminal law
If the assessment of harm exceeds 5 thousand rubles, then articles of the Criminal Code are applied. After receiving the application, a pre-investigation check is carried out, and a decision is made based on its results. If there is a composition, the material is transferred for initiation, depending on the circumstances, into investigation or inquiry. After collecting a complete package of evidence, the criminal case is sent to court. The judge makes a decision taking into account the mitigating and aggravating circumstances of the case.
Intentional commission
Article 167 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation fixes the types of liability for intentional actions aimed at partial or complete destruction of property. To bring the perpetrator to justice, the following signs must be taken into account:
- Material damage. The amount of damage must exceed 5,000 rubles. The crime is considered completed only from the moment of occurrence of illegal consequences - assessment of damage.
- Intent. The guilty citizen must be aware of the illegality of his actions and the illegality of the consequences. During pre-trial investigative measures, the official will have to confirm that the person wanted the destruction or damage of property.
- Only persons who have reached the age of 16 can be subject to punishment (when applying Part 2 of this article - from the age of 14).
Art. 167 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation consists of two parts. The second part provides for a more severe penalty and is applied if property is damaged under the following circumstances:
- from hooligan motives;
- method of commission – arson, explosion or other method dangerous to society;
- unintentional death of a person;
- infliction of grave consequences by the act (moderate bodily injury to two or more victims, severe injury to one, destruction of housing, prolonged shutdown of enterprises or shutdown of heat supply, water, etc.).
| Intentional damage to property | ||
| Types of punishment | Part 1 Art. 167 | Part 2 Art. 167 |
| Fine | up to 40,000 rubles/3 months of income | – |
| Correctional work | up to a year | – |
| Mandatory work | up to 360 hours | – |
| Forced labor | up to 24 months | up to 5 years |
| Arrest | up to 90 days | – |
| Deprivation of liberty | up to 2 years | up to 5 years |
Damage to property due to negligence
Article 168 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation establishes sanctions for the same actions, but caused without direct intent. In particular, the following signs of a criminal act must be taken into account:
- the age of the offender must be over 16 years;
- material damage occurs due to careless handling of high-risk objects (fire, vehicles, electricity, technical equipment);
- lack of direct intent, that is, the offender committed the act knowing the danger of his actions, but hoped to avoid damage.
Depending on the identified circumstances of the case, the judge may impose one of the following types of punishment:
- penalties in a maximum amount of up to 120,000 rubles (salary for 12 months);
- compulsory work (no more than 480 hours);
- correctional labor (only up to 24 months);
- up to 1 year of forced labor/restriction or imprisonment.
The subject of the crime is state or municipal property
Vandalism, qualified by Article 214 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, will be included in a special category of actions.
Vandalism in legal law is usually understood as:
- Intentional actions with the intent to cause harm. If the act was committed due to negligence, liability under Art. 214 of the Criminal Code cannot be applied.
- The subject, that is, the object to which the violation is directed, is buildings and structures, regardless of the form of ownership. This category also includes damage to state (state), municipal, and common property.
- Place of occurrence: public places or public transport.
- The peculiarity of the acts is desecration, disfigurement. That is, the object can continue to be used for its intended purpose, but the appearance of the structure (transport) is damaged.
- Only persons over the age of 14 can be punished.
Art. 214 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation consists of two parts. The first part provides punishment for a crime committed without aggravating features. The second part has qualifying characteristics for which more severe punishment is provided. These signs are:
- a group of persons takes part in the commission;
- The motive for the offense was racial and other social prejudices – discrimination.
| Damage to property due to vandalism | ||
| Types of punishment | Part 1 Art. 214 | Part 2 Art. 214 |
| Arrest | up to 3 months | – |
| Correctional work | up to 12 months | – |
| Mandatory work | up to 360 hours | – |
| Fine | up to 40,000 rubles/3 months of income | – |
| Deprivation of liberty | – | – |
| Forced labor | – | – |
| Restriction of freedom | – | up to 3 years |
Threat of property damage
There is no provision in current legislation that would provide for punishment for threatening to damage property. Therefore, it will not be possible to bring a citizen to legal liability only due to expressed threats.
Qualification of crimes
When qualifying arson, the subjective side of the offense plays a huge role, namely whether it was committed with or without intent. Let's consider both options in more detail.
Deliberate arson
Reference. Let us recall once again the meaning of the concept of “direct intent”. This is a form of guilt that has two important components: the citizen was both aware of the illegality of his act and wanted its negative consequences to occur.
Arson is considered intentional in the following cases:
- it took place using special flammable or explosive substances. All of them were brought to the scene of the incident in advance;
- improvised means (paper, gasoline) were used for the purpose of ignition;
- the offender imitated an offense using various objects (damage to wiring, electrical appliances, etc.);
- creating other conditions necessary for a fire to occur.
Unintentional arson
This includes those types of fires that occur as a result of careless handling of fire, negligence or ordinary inattention of citizens. The criminal might have known about the fire, but did not want it to happen.
Arson is considered unintentional if:
- it was caused by cigarette butts or matches left unextinguished;
- candles, torches, lanterns or other objects that use open fire were left upside down;
- the cause of the arson was a lighted fire without observing basic safety rules;
- The cause of the arson was careless handling of pyrotechnics, etc.
Civil regulation
Regardless of whether the actions of the guilty person contain signs of an administrative or criminal offense, the issue of claiming the amount of damage caused is additionally considered. Compensation for losses occurs through civil proceedings. In Art. 304 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that the owner of property (individual, organization, municipality, state) has the right to compensation for damage in court.
Art. 1084 of the designated code fixes the need to pay monetary compensation to persons who suffered from illegal actions that resulted in harm to health. The procedure for claiming funds is described in the provisions of the Civil Procedure Code.
Punishment for damaging a car
It is determined from the nature of the damage and the circumstances of its infliction - and the spread here is very large.
Anyone who breaks a tire (even with bad intentions, say, out of revenge) faces a maximum fine of up to 500 rubles. Because the repair will cost the owner less than 2.5 thousand rubles - the case will fall under the code of administrative violations.
But if restoring the car requires more than a quarter of a million, or the car is completely destroyed, or an attacker set fire to or blew up the vehicle, this is already a criminal case under the articles discussed above. After all, in addition to the two sides, there is a threat to outsiders.
Labor legislation
Clause 6 art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation stipulates the reasons for terminating working legal relations with a working citizen unilaterally at the initiative of the employer. One of these conditions is causing intentional damage to the organization’s property. Deliberate damage to property at an enterprise (or its complete destruction) can become grounds for dismissal only after the relevant court decision has entered into legal force.
Art. 238 of the Labor Code indicates which actions will be considered a labor misconduct, namely:
- deterioration of the condition of property on the company’s balance sheet;
- reduction in the number of corporate assets.
Disciplinary measures are applied as punishment. These include oral reprimands and those recorded in the worker’s personal file. The last resort, as noted above, is dismissal.
Documentary recording of the offense
The Constitution of the Russian Federation guarantees every citizen the presumption of innocence. That is, a person cannot be punished until his guilt is confirmed. To record an offense, there is a strict procedure and an established list of documents.
Reporting a crime to the police
Regardless of whether the act contains an administrative or criminal offense, the injured person must contact the nearest police station.
Important! After the application is accepted, verification measures are carried out on it, including establishing the amount of damage caused.
Most often, such checks are carried out by local police officers or detectives. The results of the preliminary check determine whether the perpetrator will be held accountable, and if so, what kind of liability it will be.
property damage statements
If a crime is established under the Criminal Code, the inspection material is transferred in accordance with the requirements for jurisdiction to the investigative unit or inquiry department to resolve the issue of initiating a criminal case.
If the offense is qualified under the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, a protocol on an administrative offense is drawn up, which, together with the collected materials, is sent for consideration to the court.
If no composition is established, the official who conducted the verification of the application refuses to initiate a case.
statements of damage to property by an unknown person
Algorithm for filing a complaint with the police:
- Collection of evidence. Evidence includes financial documents, photographs, and witness statements.
- Contact the department. This can be done in person or by mail. The Criminal Procedure Code provides for an official form of appeal (provided by police officers), but it is also possible to submit an appeal freely.
- Confirmation of acceptance of the application. After filing a complaint, the police officer gives the victim a tear-off coupon with the registration number of the complaint. Using the specified number, you can check the stage of investigation of the material.
Statement of claim to court
Dispute resolution can be considered directly in court only within the framework of civil legal relations. For this purpose, the injured party prepares a claim, which contains a detailed description of the circumstances of the damage, as well as legal requirements for the violators.
The filing of a claim takes into account the following features:
- according to the rules of jurisdiction, the consideration of the claim takes place at the place of residence of the defendant;
- an additional list of evidentiary materials is attached;
- the claim is prepared in as many copies as there are main participants in the case.
Depending on the severity of the dispute, the duration of the consideration of the case varies within six months.