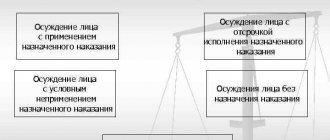
Any action prohibited by law is a violation and is divided into: crime and offense.
Crimes are listed in the Criminal Law, and violations are regulated by the Code of Administrative Offenses.
Many readers are interested in how administrative liability differs from criminal liability?
Administrative offense
According to the administrative regulatory framework, if a person commits an action contrary to the established norm, then his actions are regarded as an administrative offense.
Violation of administrative norms implies the commission of certain actions that carry consequences in the form of concern for public order.
It could be:
- being intoxicated in a public place;
- causing material damage or moral harm to other people in medium or insignificant amounts;
- disregard for prohibitions or regulations of the state system;
- partial or complete disregard of legal prohibitions.
The harm caused by such actions may be directed at society as a whole or extend to individual citizens. In these cases, although the offender poses a danger to society or others, it is minimal compared to the crime.
All administrative violations, actions and inactions, as well as enforcement measures are listed in the Code of Administrative Responsibility of the Russian Federation.
State penalties for these acts are relatively mild, these are:
- monetary fines;
- public Works;
- short period of administrative arrest.
An administrative arrest is extinguished within a short period of time and does not entail a subsequent criminal record. Administrative liability applies to all persons over 14 years of age.
Road accident
Often, administrative offenses include small or petty actions that are prohibited by law, but they do not entail consequences dangerous to society, or there could have been consequences, but did not occur.
For example, criminal and administrative liability for violating traffic rules differ.
If one or more people were killed or injured in an accident, the actions of the offender will be considered a crime and qualified according to the norms of criminal law.
If the road accident did not entail serious consequences with serious bodily injuries or death, then the perpetrator will be tried for an administrative offense, and he will be held accountable before the law under the articles of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Administrative offenses related to traffic rules often include:
- speeding on the road;
- driving a vehicle without an insurance policy or driver's license;
- driving a car without a seat belt fastened.
What penalties are provided by law for each type of criminal act?
I have already noted that crimes are actions that provide for severe punishment for the guilty person. Here it is important to correctly qualify the committed act and determine which group it belongs to. Taking into account the illegal offense in question, the penalty may be as follows:
| Offenses (administrative liability) | Crimes (criminal liability) |
| Taking into account the fact that the severity of the consequences and the degree of danger to society is minimal, the following measure can be chosen as punishment: |
- fine;
- correctional work;
- short-term arrest.
The decision with the chosen punishment option is made by the judicial authority.
The described characteristic allows us to draw the conclusion that criminal liability is a more serious punishment for the guilty person.
Crime
When a person commits a crime, he violates the norm of criminal law. At the legislative level, serious punishment is imposed for the violations of the violator. In the Criminal Code, violations are highlighted as a separate area of social relations.
A crime is considered a serious violation if it encroaches on the following areas of life:
- established public legal relations;
- human freedom and personal rights;
- property of the state, organizations or individuals;
- area of public administration;
- constitutional system of the state.
Crime has many classifications, the main parameters of which include the degree of danger to society.
For example, murder poses a greater danger to society than theft or slander. Accordingly, the punishment for murder will be more severe.
The same theft can occur in various ways. Secret theft carries less danger, since it occurs without contact with the owner of the property, causing only material and moral harm. In the case of open theft of property, a robbery occurs that has a threat of harm to human health and life.
Although the crime has one qualification - theft, its methods of execution are different, which leads to different degrees of public danger, and the punishment will also be different.
Differences between an offense and a crime
The main criterion separating a violation of law from a crime is the danger to surrounding people and society. The Criminal Code is based on the severity of the act and the severity of the consequences from the established norm.
After establishing the degree of danger to society, the rule of law that the guilty person violated is determined by establishing additional criteria, these are:
- presence of intent (done accidentally or on purpose);
- level of involvement of the suspect (direct or indirect);
- area of legal relations, sphere of law.
The legislator divided public danger into two levels:
- High . If the crime falls within the criminal legal sphere.
- Low . If the violation of the law relates to the administrative-legal area.
In Part 1 of Art. 14 of the Criminal Code of Russia contains a list of actions and inactions of a person from these two areas of law. It also indicates the responsibility that the guilty person will bear.
The criminal and administrative liability of minors differs. The criminal branch is distinguished from the administrative sphere by the age when a guilty person can be brought to justice.
At what age does responsibility for actions begin? In criminal law, only a person who has reached the age of 16 can stand trial for a crime, and not before. According to administrative regulations, a person over 14 years of age can be charged for a violation.
There is another dividing barrier between these concepts: the goal and motive of the offender. For example, let's take such a violation of the law as moonshine.
If it was manufactured by a person for the purpose of sale, then the actions will be qualified as a crime, since the purpose and motive of the act that prompted the violation of the law is to increase one’s own capital.
If the accused has violated the law for his own use, this will be considered an administrative violation. There was no purpose in this act, but only a motive.
But one must also take into account the scale of the consequences: the production of prohibited products for one’s own needs in small quantities, and for sale – production in especially large quantities.
Similarities between crime and delinquency
In addition to the differences, there are common features between these two concepts that imply a violation of the norms established by the state:
- All actions entail consequences to varying degrees for the individual or society.
- Punishment is provided for all illegal actions.
- Every violation must be recorded and proven.
In addition to punishing the perpetrator, the criminal sphere performs a protective function, since the citizen who has committed a crime is isolated from society, which means that other persons will be protected from danger and further commission of all kinds of illegal actions.
All offenses have fundamental functions:
- regulation of legal interactions between government bodies and citizens;
- protection of public order within the country;
- preventing illegal acts in the future.
What information can be called defamatory?
We are talking about information that can spoil the reputation of an opponent, cause general censure, harm business, etc. The following information is considered defamatory:
- about the presence of a sexually transmitted disease;
- about violation of the law;
- about alcohol or drug abuse;
- about committing an immoral act;
- about poor performance of functional duties at work, etc.
To bring the slanderer to justice, a citizen must contact the nearest police station. Here he writes a statement in which all the circumstances of the case should be stated.
Simultaneous attraction
Is it possible to bring administrative and criminal liability at the same time? In accordance with Part 2 of Art. 6 of the Criminal Code and Part 5 of Art. 4.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses, no one can bear criminal and administrative liability twice for the same offense.
According to clause 7, part 1, art. 24.5 of the Administrative Code, administrative proceedings cannot be initiated if there is a decision to initiate a criminal investigation. If production has already begun, it should be stopped.
However, in the legislation of the Russian Federation there is no direct prohibition on initiating a criminal case when administrative proceedings have begun . It is also necessary to take into account the signs of the objective side and the composition of some offenses and crimes.
For example, it is permissible to simultaneously bring the perpetrator to administrative and criminal liability in cases of violation of traffic rules, when a person in a state of intoxication caused serious harm to a person’s health through negligence, which resulted in death.
Beatings
Is beating a criminal or administrative liability? Battery is a criminal offence. Battery includes violent acts without consequences, but resulting in physical pain.
They can be committed out of hooligan motives, as well as because of religious hatred, racial or political hostility.
In order for criminal liability to be replaced by administrative punishment, the victim must not be related to the bully, and also not be a disabled person, an elderly person, a pregnant woman or a minor teenager.
The court also takes into account whether the crime was committed for the first time, the accused did not cause significant harm to the victim’s health, and the actions were not intentional.
These circumstances can mitigate the sentence of the perpetrator and replace criminal proceedings with administrative punishment.
Fight
Many are also interested in whether fighting is a criminal or administrative offense? If responsibility for beating depends on the circumstances and severity of the injuries, then the fight is already intentional.
In the Criminal Code, damage is distinguished:
- light – up to 2 years in prison;
- average – up to 5 years of imprisonment;
- serious - up to 15 years of imprisonment.
In case of damage of mild or moderate severity, a pre-trial reconciliation procedure is possible, then the conflict can be resolved without criminal proceedings.
Administrative fine up to 40 thousand rubles. can be obtained only if health problems do not occur after the fight.
If there is a fight on the street with a passerby who is not a relative of the hooligan, and he was not seriously injured, then the attacker faces administrative punishment (if the violation occurred for the first time).
Criminal punishment cannot be avoided if it is proven that the damage was caused on the basis of religious and ethnic hatred.
The severity of the punishment depends on the circumstances . For example, a son beating helpless parents, a fight while drunk, or a crime against children forces the court to impose a harsher punishment.
For a group beating you can get up to 5 years in prison, and even more if using a weapon.
Serious injury is considered harm that would lead to death of the victim in the absence of medical care, without which people die in half of the cases from serious bodily injury.
If this happens, the accused will be given a maximum sentence of up to 15 years in prison.
What is libel
The concept of slander is enshrined in Article 128.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. We are talking about the dissemination of deliberately false information that affects the honor, dignity or reputation of a person.
A slanderer can be brought to justice if the following grounds exist:
- The culprit understands that he is spreading false information. If a citizen unintentionally slandered another person, he will not be punished for his actions. For example, the slanderer could sincerely believe in the veracity of the information presented.
- False information undermines the victim's reputation and affects her honor and dignity. If the statements are neutral or are a subjective opinion, then there can be no talk of any slander. For example, statements that a neighbor dresses tastelessly cannot be called slander. This is a personal opinion, the expression of which is not prohibited in the Russian Federation.
- The slanderer must spread false information among a certain group of people. For example, making a statement at a meeting of company employees or giving an interview on television. Dissemination of information on social networks is also considered libel. But information expressed during a confidential conversation is not slander.
- Presence of direct intent. The slanderer must spread information, wanting to discredit the victim and humiliate her.
Thus, there is no punishment for disseminating defamatory but true information.
Arbitrage practice
Evidence of the commission of illegal acts is sufficient grounds for applying to the accused the punishment provided for by the norms of the code.
The Administrative Code contains types of punishment for minor violations committed by unreliable individuals, for example, persons without a fixed place of residence or alcoholics.
This code contains descriptions of offenses from various areas of jurisprudence: the judicial system, tax, labor and civil spheres, management of the traffic police.
All violations established at the legislative level are dangerous to society . It is impossible to even imagine what would happen if all people did as they pleased.
Therefore, the types of responsibility specified in the code are intended to remind citizens what awaits them for violating the rules of conduct. In judicial practice, there is a very small percentage of administrative and criminal cases where the court acquits the offender.
Exceptions to the rules
In the field of state punishments, conditions and principles are equal for everyone, but there are still a few exceptions. For example, for organizations or legal entities.
With varying severity of the act, the organization can be brought not only to administrative, but also to criminal liability.
Administrative liability may be imposed on the company or its officials. In criminal law, only the proper person can be punished, but not the company.
The same type of offenses with varying degrees of severity are:
- Disciplinary offense . Refers to the norms of labor law, the culprit will be held accountable in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. With the participation of officials, the case will be considered as an administrative case.
- Hooliganism . Minor hooliganism is punishable by administrative liability, and hooliganism of moderate severity and above is subject to criminal punishment.
- Theft . For petty theft, they will not even initiate a case, but for large-scale theft, it will be considered based on the method of commission and by whom it was carried out.
There are disputes among experts about the repeated violation of administrative norms, and whether this is a characteristic of the personality of the perpetrator or a basis for reclassifying an administrative offense into a criminal case.
The legislation believes that repeated offenses should be considered a crime and punished under the Criminal Code.
For example, let's take a common violation - driving a vehicle while intoxicated . If previously the offender was deprived of the right to drive a car for several years, now he will face imprisonment.
Before these changes were made, the court could prohibit the same person from driving a vehicle, and under this article, with multiple punishments, a total term of 8-10 years without the right to drive a car was added up.
It should be remembered that jurisprudence in 2022 has not yet been thoroughly developed. Various acts related to judicial practice and precedents are supplemented, changed or terminated.
To separate administrative responsibility and crime, it is enough to have an idea of the differences between them and to be aware of the degree of severity.
The difference between these areas lies in the severity of the punishment, depending on the types of violation and the norms of behavior established in society.