What is innocent tort?
Innocent harm should be understood as:
- An act is committed innocently if the person who committed it did not realize and, due to the circumstances of the case, could not realize the social danger of his actions (inaction) or did not foresee the possibility of dangerous consequences and, due to the circumstances of the case, should not or could not have foreseen them.
- An act is considered committed innocently if the person who committed it, although he foresaw the possibility of dangerous consequences of his actions (inaction), could not prevent these consequences due to the inconsistency of his psychophysiological qualities with the requirements of extreme conditions or neuropsychic overload.
We will consider the types of incidental situations with their examples below.
Types of incidents in criminal law
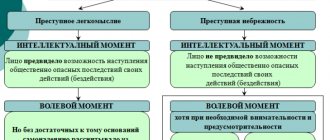
From the definition of two parts of Article 28 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, at least three types of incidental situations can be distinguished. Let's look at each criminal case using examples.
Case 1. The person did not and could not realize the criminality of his actions (inaction)
Example. A work colleague, a neighbor at the place of residence, or another acquaintance, under some pretext, asks the citizen to receive a parcel for him, pick it up from the conductor of car No. 6 of the Nursultan - Chelyabinsk train and transfer it to a person named Vladimir at the specified address. The package is not heavy - only 2 kilograms. The citizen conscientiously fulfills the request of his friend, most likely even absolutely free of charge, and two days later he finds himself interrogated by an investigator of the Investigative Committee of the Russian Federation.
The fact is that a citizen’s fingerprints were found on the package and the neighbor identified him as the person who came to Vladimir’s apartment two days ago. It turns out that Vladimir died from an overdose of the narcotic drug “Spice,” which was found right there in his apartment, in the same package.
Explanation. Formally, the citizen’s actions show signs of several elements of crime at once - smuggling (since the train is from Kazakhstan), transportation and preparation for sale of narcotic drugs on a particularly large scale and possibly causing death through negligence of Vladimir, punishable by up to 20 years in prison.
In fact, in this situation, the citizen’s actions lack such an important sign of a crime as guilt. The citizen did not know that there were drugs in the package and could not be aware of the criminality of his actions when handing over and transporting the package. And he is not liable for the listed crimes.
Moscow
Saint Petersburg
Free consultation
Moscow
Saint Petersburg
Example. The dispatcher of a hazardous production facility, having started his shift, checked the serviceability of the equipment and carried out all the necessary actions prescribed in his job description. After some time, the technological equipment explodes. Two people died. During the investigation, it was established that the explosion occurred as a result of excess gas pressure in the system, which had to be released manually. There is inaction of the dispatcher.
But it was also found that the reasons contributing to the explosion were a malfunction of the pressure gauge and the emergency warning system, which was supposed to signal the dispatcher about the need for action.
The dispatcher saw normal instrument readings, the warning system was silent, and accordingly he did nothing. His inaction is not to blame.
Case 2. The person did not foresee the possibility of dangerous consequences and, due to the circumstances, could not and should not have foreseen them
Example. The driver brakes sharply, trying not to hit a pedestrian who unexpectedly stepped onto the roadway. As a result of such braking, a massive traffic accident occurs with cars traveling in the same direction, as a result of which people die. Explanation. The driver does the right thing in this situation, perhaps even saving the pedestrian's life, but others die. Dangerous consequences in the form of death occurred, but the driver could not foresee them. He is not guilty, he is not liable.
Case 3. A person foresees the possibility of dangerous consequences of his actions, but due to the inconsistency of his psychophysiological qualities with the requirements of extreme conditions or neuropsychic overload, he could not prevent these consequences
Example. Again, a fairly common picture is a pedestrian suddenly appearing on the roadway in front of a moving car at night, wearing dark clothes, in a state of intoxication and at a distance of 5-10 kilometers from a populated area. Very unexpected for the driver. Explanation. The driver of any vehicle must always anticipate various situations on the road. But in the described conditions, the appearance of a pedestrian will obviously create a state of stress for the driver to one degree or another, and perhaps he will not be able to cope with this state and will hit a person.
The case falls under the third type of incident. The driver is not at fault and is not liable.
Let's change the situation a little with the explosion in production.
Example. The dispatcher, by order of the facility manager, remained at work for the second day. There was an equipment breakdown, a single signal was sent to the control panel about an increase in pressure in the system, the dispatcher, due to fatigue, did not react in time - an explosion occurred, harm was caused to health and people died. Explanation. Most likely, the dispatcher is not at fault in this situation, and he is not liable. Unlike the person who gave the order to start working overtime and without rest.
Characteristics of varieties
The first type of innocent harm, which is regulated by Article 28 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, excludes the criminal liability of a citizen for his actions due to the fact that the person did not realize that the act he committed could lead to dangerous consequences.
Such dangerous situations include cases where people suffer and die as a result of accidental actions . For example:
- As a result of an accident on the road, the unconscious driver was trapped in a car that caught fire.
A young guy rushed to his aid and, using physical force, began jerking the victim out of the car. Having freed the driver, he pulled him away from the burning car and called an ambulance. But by the time the doctors arrived, the victim died as a result of rupture of soft tissues and arteries. Having shown courage and rushed to help the victim, the young man did not realize that his actions to save the person would serve as the true cause of death of the driver of the vehicle. Investigators, of course, will not find any crime in his actions. - Returning home late in the evening, the owner of the apartment noticed a strong smell of gas in the living room.
Deciding to establish the reason, he arbitrarily pressed the switch at the front door. An explosion was heard, the ceiling collapsed, neighboring apartments were damaged, the residents of which, like the owner himself, received serious burns and injuries of varying severity. The homeowner’s actions were usual: he came home and turned on the light. The person did not realize that a spark that accidentally slipped when turning on the light could cause a big disaster, where he himself, as well as the people living nearby, would suffer. But the citizen’s actions do not constitute a crime, and he will not incur criminal liability.
The second type of innocent harm involves the inability of a citizen to foresee a sudden danger as a result of his actions. Examples of such cases are not uncommon and are very common in our daily lives.
- A car that suddenly braked, due to a pedestrian quickly running out onto the roadway, caused a collision of several cars following it at once, where people died.
By saving the life of the pedestrian, the driver did the right thing, but in the current extreme situation it was impossible to foresee the emergency situation that had arisen with the cars driving behind him. A tragedy occurred that claimed human lives, but there is no corpus delicti in the actions of the driver who suddenly braked, and Article 28 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation exempts the citizen from criminal liability. - A cigarette butt accidentally thrown into an empty barrel caused a tragedy, as a result of which a person passing by died.
Gasoline vapors accumulated in an empty container caused an explosion, and pieces of metal flying in all directions mortally wounded a passerby. The culprit of the tragedy himself also suffered, but just as in previous cases, there is no corpus delicti in the person’s actions. The citizen could not have foreseen the dangerous situation that would result from his action.
The third type of innocent harm, which is reflected in Article 28 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, is characterized by special cases where, as a result of actions or inaction, a citizen can foresee the creation of a dangerous situation.
It may be impossible to prevent a tragedy due to various reasons caused by high nervous stress, mental disorder, or the absence of certain psychophysiological qualities in the current situation.
An example would be extreme cases and prevailing circumstances that preclude a citizen from taking the necessary measures to prevent a dangerous situation. For example:
- A pedestrian suddenly running out in front of a car in a place that is not intended for crossing the road can be predicted, but a collision with a person in this case is almost impossible to prevent.
A suddenly created extreme situation leaves no time for thought, the driver instantly and unexpectedly receives great nervous strain and stress, and it is possible to avoid a tragedy only by luck. There is no corpus delicti in the actions of a driver who quickly braked but hit a pedestrian, and he does not bear criminal liability for his actions in such a situation. - A person working two shifts in a row under the orders of the administration has all the signs of overwork and is unable to adequately assess and respond to his actions.
In extreme circumstances, where harm will be caused to other citizens, this fact will be taken into account by the investigation, and a particular citizen may not bear criminal liability for his activities.
At first glance, all three types of innocent harm contain some elements of negligent behavior and careless actions, but they are not considered negligence after a detailed expert analysis and thorough investigation.
Be prepared for the fact that in some cases you will not be able to prove your innocence. Depending on the type of damage caused, you will be given the appropriate punishment:
- Causing grievous bodily harm: through negligence and in a state of passion.
- Causing average harm to health through negligence and unintentionally - here.
- Causing slight harm to health through negligence and unintentionally - more details here.
Difference from criminal negligence (carelessness)
The concept of innocent causing of harm should be strictly distinguished in its content from causing harm by negligence, regulated by Article 26 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
The main difference here is the presence of guilt in the actions of a person , as a sign of a crime, although there is no intent to cause any harm.
A person who commits a crime through negligence is aware of the possibility of socially dangerous consequences as a result of his actions or has the ability to foresee the occurrence of dangerous consequences.
Let's change the example a little about receiving a package at the request of a friend.
Example. The citizen knows that the friend who asked him to receive the package is a drug addict. On the way, the package falls to the ground, the packaging is torn, and the citizen sees characteristically packaged bags with a substance of plant origin. Despite all this, the citizen delivers the package to Vladimir, who then dies from an overdose. Explanation. Most likely in this situation, the citizen may be charged with the above-mentioned crimes, including careless causing of death.
Another change of script.
Example. The manager of a hazardous production facility sees how the instruments twice show that the pressure is exceeding the norm and then again the norm. In such cases, the job description requires certain actions to be taken by the dispatcher. You need to go into the workshop and check the two shut-off valves. Record your readings and your actions in a journal. The consequences of a malfunction of the valves are quite known to the dispatcher due to his work experience - an increase in pressure and a possible explosion. The dispatcher does not go anywhere hoping that the instruments have made a mistake and everything is in order. The result is known - an explosion with deaths.
Explanation. The dispatcher is guilty of carelessly causing death as a result of improper operation of equipment, as a result of which a criminal case is initiated and a trial is initiated.
Example. A pedestrian who suddenly appears on the roadway in front of a moving car at night, wearing dark clothes, in a state of intoxication and at a distance of 5-10 kilometers from a populated area. Very unexpected for the driver. Collision and corpse. The incidental situation already described above - with one thing, but.
During the inspection of the scene of the incident, the braking distance of the car was found to be significantly greater in terms of characteristics than the braking distance of a car moving at the permitted speed on this section of the road. An automotive technical examination showed that the on-board computer recorded the speed at the moment of the collision as 125 kilometers per hour, and the average speed over the last period of time was 110 km.
Explanation. As a result, the situation from an innocent incident turned into a completely real criminal case under Art. 264 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation and further court. And the person who committed the crime may even lose his freedom.
Moscow
Saint Petersburg
Free consultation
Moscow
Saint Petersburg
Evidence that a person is innocent of causing harm
In order for Article 28 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation to fully work, and for a respectable citizen to be protected by the law, very high-quality work by the investigative authorities is necessary. The desire of the person conducting the investigation or preliminary inspection to establish the truth, as well as his sufficient qualifications.
Starting from the initial actions at the scene of the incident and ending with the various necessary examinations during the investigation.
Many incidents are investigated precisely within the framework of initiated criminal cases, since it is necessary to carry out complex measures and various examinations, which are not always possible to carry out as part of a preliminary inspection. Subsequently, when all the circumstances are clarified, the criminal case is terminated.
7(800) 350-23-68
Dmitry Konstantinovich
Expert of the site "Legal Consultant"
Ask a Question
Based on the principle of presumption of innocence, a person is not required to prove his innocence. And only the court recognizes him as guilty. These slogans of criminal law are well known and basically work, like the fairness of our justice. But you shouldn’t sit and hope for justice if you see that something is going wrong. It was not for nothing that I gave several examples in the paragraph above and tried to show how borderline the situation of innocent and careless causing of harm is.
I don’t want to question the competence of the investigative authorities, but if you suddenly find yourself in one of these unpleasant situations, you don’t need to wait for a probable or random outcome. Contact a criminal defense attorney who is knowledgeable in criminal law. The sooner a lawyer gets involved and familiarizes himself with the situation, the better.