For damage to common property, you can receive an administrative fine - from 300 to 500 rubles (Article 7.17 of the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses). They will be held accountable for intentional actions that did not cause significant damage, which starts from 5,000 rubles. Roughly speaking, if someone damages common property within this amount, they will receive an administrative fine. If he “goes wild” for a large amount, he will receive punishment under Art. 167 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. A fine can be imposed, for example, for a broken window in the entrance, a broken button for calling the elevator, inscriptions and drawings on the walls.
Let us give two examples from judicial practice when citizens were brought to administrative responsibility for damaging common property.
What is damage to common property?
The common property of residents is what is included in an apartment building, but does not belong to any of them, according to official documents, for example, like an apartment. This concept is enshrined in housing legislation.
In the event that a breakdown or damage to such property occurs, you need to contact the company performing management functions. They have an obligation to repair, replace or correct a thing that has been rendered unusable. This obligation arises for the management company due to the fact that the residents of the house pay monthly utility bills.
Responsibility established in relation to minors
A crime such as damage to property in an apartment building implies the possibility of establishing liability in relation to persons under the age of majority. If the offender is not yet 14 years old, his parents or legal representatives will be responsible for his unlawful actions.
If a person has already reached 14 years of age, full measures of responsibility can be applied to him, on an equal basis with adults. In the event that the authorized body imposes a fine and the perpetrator does not have a source of income, financial obligations are assigned to his parents or guardians.
If damage to property in an apartment complex was accompanied by certain aggravating circumstances and entailed the need to apply criminal liability measures, they can only be established if the defendant has already reached 16 years of age.
Removal of liability from the guilty person will be possible only if the damage to valuables was caused by an incapacitated person. This fact must be confirmed by relevant evidence - medical certificates, court reports and other documents.
Author of the article
Dmitry Leonov
Work experience 15 years, specialization - housing, family, inheritance, land, criminal cases.
Author's rating
721
Articles written
712
about the author
Classification
Property located in an apartment building may have the following types:
- Premises that are not included in the apartment. These include attics, elevators and equipment for them, stairs and flights, corridors, basements. Despite the fact that in new buildings the ground floors are sold and used as premises with non-residential purposes, their parts where communications are located belong to the common property.
- Premises that are located in the house and do not belong to anyone, according to official documentation. You, together with other residents of the house, can equip a gym in the basement, while ownership will not belong to any of you, that is, anyone can use it.
- Structures that have load-bearing value, roofs, or equipment located in the house itself or outside it. Provided that it is used not by one apartment, but by several.
- The land on which the house structure is located. This also includes elements that have as their function landscaping, parking, playgrounds, etc. Boundaries are determined in accordance with the legislation in force in urban planning and land development.
Careless damage to someone else's property
It is logical that the legislator provided for liability for damage only to someone else’s property. In fact, it would be absurd to punish a person who decided to destroy his objects and belongings for reasons known only to him. At the same time, there is always a danger that by setting fire to one’s own, harm will be caused to others. In this case, the Criminal Code provides for an article that provides for the possibility of bringing to liability for destruction or damage to property through negligence. The condition for this is:
- the value of damaged property of other citizens exceeds 250,000 rubles;
- the crime was committed as a result of handling fire or another source of increased danger.
Since such a crime is considered careless, the punishment for it is relatively mild: a fine of up to 120,000 rubles, community service, and imprisonment for up to 1 year .
Example No. 5 . Having quarreled with his wife, V.V. Kuznetsov, being extremely intoxicated, set fire to his own house so that during the divorce it would not go to his ex-wife. The fire spread to the outbuildings of the neighboring plot, as a result of which the garage and bathhouse of neighbor E.M. Kravtsov completely burned down. The careless actions of Kuznetsov V.V. the neighbor suffered damage in excess of one million rubles. The culprit was sentenced to a fine of 100,000 rubles; the claim for compensation for the value of lost real estate was satisfied in full.
Where to file a complaint
Speaking about where you can apply if the type of property in question has been damaged, it is worth paying attention to how the crime is qualified . The assessment may be carried out under criminal or administrative law. In cases where consumer rights are violated, the law “On the Protection of Consumer Rights” is used.
Let's consider the grounds for qualifying acts:
- If the property was damaged or completely destroyed, and the amount of damage is large, then the assessment takes place under Article 167 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. Please note that in 2016, amendments were made to the legislation, according to which major damage will be in the amount of five thousand rubles. The complaint must be filed with the police department. You can contact the nearest branch. Please note that if you apply to a location other than your registered address, the processing will take longer.
- When the damage is caused by accident, liability is provided under Article 168 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, the appeal is also made to the police.
- If an offense is committed, which is assessed under administrative law, then the amount of damage caused as a result of damage should be insignificant. In this case, the application is submitted to the police department.
- If the police refuse to accept your appeal, you can write a statement to the prosecutor's office.
- If it is necessary to compensate for damage caused by an unlawful act, you should contact the judicial authorities. You can make a similar claim in criminal proceedings, but to ensure you receive compensation, you should file a civil claim separately.
Who to complain to
Where to go if hooligans have damaged the property of an apartment building? First of all , you need to write an application to the management company that services this house. There they will accept the complaint and draw up a report.
The next step is the local police officer. His task is to open a case of an administrative or criminal offense. He will also look for violators if they are not known to the applicants.
How to find the culprits? Witnesses or CCTV footage will help. When the suspects are identified, a criminal case is initiated. And then the court will issue an appropriate verdict.
But very often it is quite difficult to find the perpetrators. If all attempts are unsuccessful, the matter will not progress further. There will be no one to punish.
How to write an application correctly
The form of the document in this case depends on where you will apply. When contacting the police, it is not at all necessary to write a complaint at home. You can contact the employee and explain what happened, he will fill out a protocol based on your words, which you will need to read and, if everything is correct, sign.
It is also possible to write an application yourself. You can do this at the police station or at home. In both cases, it is best to use a sample. In law enforcement agencies it is located on the information stand.
Important! If you submit a ready-made application, be sure to take a coupon from the receiving employee, which indicates the registration number.
If you file a claim in court, you must prepare a document in advance and submit it to the office. It must indicate:
- name of the judicial authority;
- full details of the sender, including contact telephone number;
- the essence of what happened (indicated in detail);
- the amount of damage caused;
- confirmation of this amount;
- The documentation is attached and executed in the form of attachments:
- the signature and date are indicated at the end of the document.
The claim must be filed in the place where the defendant is registered, or at his location. This rule is established by procedural laws.
How does the law work?
Damage to property means unintentional or intentional damage to someone else's property, which has value and material expression. At the same time, it is important to know the difference between the main terms used when considering this type of case - damage and destruction of a thing:
- If damaged, a thing loses its properties to one degree or another and becomes partially unsuitable for use for its intended purpose.
- When destroyed, it becomes completely unsuitable for further use.
According to legal norms, a citizen or organization whose property was damaged is recognized as a victim and has the right to file a lawsuit for compensation for damage and a statement to the police demanding that the offender be brought to justice in accordance with the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
What responsibilities are provided?
In this case, it does not matter who committed the offense; it could be a citizen of our country, Ukraine or a stateless person. As already indicated, the assessment can be made according to criminal or administrative standards. In the latter case, the amount of damage does not exceed five thousand rubles. A fine is imposed, the amount of which varies from three hundred to five hundred rubles.
If a crime is committed, the fine increases to 40 thousand rubles. In this case, imprisonment of up to five years can also be applied. This measure is applicable to persons who were guided by hooligan motives, or as a result of their actions, grave consequences occurred.
Explosion and arson as ways to destroy property
Explosives are used mainly to destroy cars - such crimes were not uncommon in the 90s, and such cases still occur today, especially among businessmen and influential people. Also, the destruction of cars in this way can take place if there is a national motive - there are known cases when only cars of a certain region (for example, the Caucasus) or republic were blown up by the perpetrators. Since the national motive is not directly provided for in the article of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, such circumstances are additionally recognized by the court as aggravating when passing a sentence.
Destruction or damage to property by arson is usually committed in relation to detached real estate - houses, kiosks, garages. In practice, there are cases where arson is a way of concealing another, more serious crime.
Example No. 3 . Seller I.I. Pavlov, working for entrepreneur A.A. Skvortsov. under an employment contract at a food kiosk, he made a large shortage due to his own fraud with invoices. When this became known to the employer, Pavlov I.I. staged an arson, denying his involvement in the destruction of the kiosk (it was burned to the ground), even being the first to arrive at the scene to assist in extinguishing the fire. Thanks to the external surveillance cameras with which the nearby building was equipped and about which Pavlov I.I. had no idea, the police determined that he had committed the arson. With the help of complex comprehensive examinations, the amount of the shortage and the flammable substance used by I.I. Pavlov were established. As a result, the culprit was punished with a long term of imprisonment under two articles of the Criminal Code - for destroying a kiosk by arson and deliberate embezzlement of entrusted property. Example No. 4 . To the convicted Rykov A.P. was sentenced to 18 years in prison for the fact that while drinking alcohol in the house of Lobanov G.G. he inflicted several stab wounds to the latter in the heart area, as a result of which the victim died on the spot. To hide the traces of a particularly serious crime, Rykov A.P. I couldn’t think of anything better than to burn the house where the corpse was. Rykov A.P. doused the household with kerosene from all sides and set it on fire. The crime was solved without delay, as eyewitnesses were found. Subsequently, Rykov wrote a confession, unable to cope with the feeling of guilt. At the court hearing, the claim of the relatives of the murdered man to recover the cost of the burned house from the perpetrator was satisfied.
Other generally dangerous methods of intentional damage or destruction of property are quite rare in practice. For example, this could be the use of homemade shooting devices that create a danger to others, mechanical units used for other purposes than their intended purpose, etc.
As a result of the actions of those who deliberately damage other people's property, the death of strangers or other tragic events sometimes occur. The Supreme Court explained that these may include causing significant harm to health, including to several persons, causing disability, depriving people of shelter or livelihood, prolonged downtime of large enterprises, etc.
Common property in an apartment building
First, let's figure out what common property is and who is obliged to maintain it in proper condition. Common property includes:
- stairs;
- elevators and elevator shafts;
- attics;
- corridors;
- technical floors;
- basements;
- inter-apartment landings;
- roofs;
- electrical, mechanical equipment (for example, ramps);
- enclosing load-bearing structures;
- other premises intended to meet the social and everyday needs of residents.
Owners of residential premises own, use and dispose of common property on the basis of an agreement reached between all owners at a meeting, and are also responsible for the proper maintenance of common property.
Do you have any questions?
To get the most detailed advice on your issue, you just need to follow any of the suggested options:
- Request a consultation using the form
on our website - Or just call the number: 8 800 350-83-74
What to do in case of acquittal
An acquittal is rendered in the following cases:
- the victim’s property was partially damaged or destroyed as a result of military operations related to hostilities or natural disasters;
- the non-involvement of the accused in the incident was confirmed.
In such situations, the court has the authority to refuse to satisfy a civil claim for damages.
Criminal liability is removed in the absence of evidence of involvement in criminal acts (in this case, the law on the presumption of innocence comes into force).
Who will determine the price of lost things?
Determining the cost of damage is the competence of an appraisal examination, which is appointed as part of the preliminary investigation. As in other categories of cases, the expert assesses the market value at the time of loss or damage, taking into account wear and tear and the possibility of restoration. Most often in criminal cases, the subject of assessment is:
- cars. Particular difficulty in establishing the cost of damage caused occurs in cases in which the car is burned. In such cases, the expert turns to official data on the average market value of a car in a particular city, taking into account reliable characteristics provided by the victims: year of manufacture, period of ownership, information about accidents, make of car, etc.;
- expensive equipment. The expert takes into account the name of the manufacturer, data on the technical condition of the object, etc.;
- real estate. The assessment is carried out according to the cadastral value on the day the crime was committed (in case of complete destruction) or, if part of the house is damaged (doors, windows, interior decoration), then the calculation takes into account both the cost of restoration work and the possibility of using the premises before they are completed;
- expensive goods (fur items, clothes made of genuine leather, etc.) - the cost of damage is determined mainly by the receipt provided by the victim - almost always receipts for the purchase of such items are stored, taking into account the length of the expiration date.
So, based on the conclusion of the assessment examination, police officers make a conclusion about whether in each specific case there are grounds for initiating a criminal case. If there are such grounds (the amount of damage exceeds 5,000 rubles and is significant for the victim), the actions of the perpetrator will be given a legal assessment under part one or two of Article 167 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
In order to determine damage, the approach defined in the notes to Article 158 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation is applied.
- Significant damage to a citizen is determined taking into account his property status, but cannot be less than five thousand rubles.
- Large size is the value of property exceeding two hundred and fifty thousand rubles, and especially large - one million rubles.
Often the investigation authorities miss one important detail when establishing the significance of the damage.
Significant damage to a citizen is determined from several criteria, and not simply from the value of the property:
- the cost of destroyed property or the cost of restoring damaged property - cannot be less than 5,000 rubles (always observed)
- the significance of this property for the victim (for example: it has memorable value, a family heirloom)
- mandatory study of the victim’s type of activity and financial situation, taking into account all his income (precisely all income, and not from one source; often the victim’s property status is not clarified, limited to his explanations)
If all the income of the victim and the significance of the property for him are not established with reliable accuracy, the court decision cannot be recognized as legal, since there is no establishment of an important criterion - significance.
Agree that for one citizen with an income of 100,000 rubles a month, it is doubtful that damage of 10,000 rubles would be considered significant based on the cost of harm criterion alone, but the picture changes if the entire income of the victim is 8,000 rubles.
In another situation, if the victim himself tried to throw the property into a landfill, or, for example, treated it with disdain, it is impossible to impute damage only according to the criterion of the value of the property, because in this case, the actions of the victim indicate the lack of significance of the property for him, and as a result, the absence sign of a crime as the significance of the damage.
In order to apply this approach, there is a direct indication of clause 6 of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated 06/05/2002 No. 14 “When deciding whether significant damage has been caused to the owner or other possessor of property, one should proceed from the value of the destroyed property or the cost of restoring damaged property, the significance this property for the victim, for example, depending on the type of his activity and financial situation or financial and economic condition of the legal entity that was the owner or other possessor of the destroyed or damaged property.”
An example from judicial practice is: Resolution of the Presidium of the Moscow City Court dated June 19, 2008 in case No. 44у-322/08
“...From what was presented by the victim A.B. The expert's conclusion shows that the estimated cost of restoring the car is 18,161 rubles 26 kopecks (case sheet 66 - 84). As can be seen from the reasoning part of the verdict, the court recognized the damage caused to A.B. the damage was significant only on the basis of the opinion of the victim himself, who claimed that he was unable to repair the car due to the lack of necessary funds. At the same time, the issue of the victim’s property status was not clarified by the prosecution and an assessment of this circumstance in comparison with data on the cost of restoration of the car according to any objective criteria was not given. Therefore, the court’s conclusion about the significance of the damage caused to the victim and the presence in this regard of A.’s actions constituted a crime under Art. 167 part 1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation cannot be considered sufficiently motivated...”
How to assess damage
To make a decision on the case under consideration, the injured party will need to provide human rights authorities with information about the price of the destroyed property or the cost of restoration work. In situations with arson, flooding of apartments, and intentional damage to cars, it is recommended to use the services of experts. After the survey, appraisers clarify the amount of losses.
Estimation of the amount of damage.
If the damage is minor and paying for an expensive examination is not practical, the victim can himself assess the extent of damage to personal property. To do this, you will need to find similar items for sale and find out their market price or present copies of receipts and certificates of acceptance of restoration work.
The legislative framework
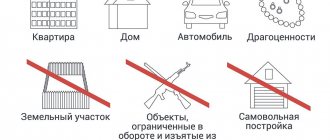
A number of property assets are in the personal possession of Russian citizens:
- real estate;
- personal vehicles (cars, motorcycles, mopeds, scooters, etc.);
- antiques, paintings by famous artists and other interior items.
Intentional or unintentional violation of their integrity is defined by law as damage. It can have 2 degrees:
- Partial. It manifests itself as incomplete damage to property with the possibility of restoration through repair or restoration.
- Full. Expressed by final destruction or destruction.
Federal laws.
Intentional damage to property belonging to individuals is regulated by Article 167 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. The legislative act specifies the sanctions imposed on the offender when his guilt is confirmed in court.
Responsibility and penalties for unintentional damage to personal property of citizens are discussed in Art. 168 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
To open a criminal case regarding the crime in question, it will be necessary to estimate in monetary terms the amount of harm caused. Procedural proceedings begin in the following cases:
- the cost of property damaged as a result of the deliberate actions of the offender is at least 2,500 rubles;
- damage caused unintentionally is estimated at an amount exceeding 250 thousand rubles.